🔧 Transforming BC Error Handling with Smart Recommendations 📝(English version)
🔧 Transformando el manejo de errores en BC con recomendaciones inteligentes📝
Seguiremos con el tema de la gestión de errores y como podemos aprovechar los patrones y funcionalidades que ofrece Business Central, ahora exploraremos la aplicación (extensión) de «Error Messages with Recommendations« de Microsoft, una funcionalidad muy útil y con muchas posibilidades, nos permite transformar un mensaje de error en una solución inmediata del error con un clic.
La página centralizada «Error Messages» actúa como el centro de control donde los usuarios pueden ver todos los errores y ejecutar acciones correctivas directamente. Esta aplicación nos permite crear extensiones que capturen errores automáticamente y ofrezcan soluciones inteligentes. La aplicación permite:
- Detectar automáticamente el problema específico.
- Sugerir una acción correctiva clara.
- Permitir la corrección inmediata con un solo clic.
- Confirmar la solución con un mensaje de éxito.
Podríamos mostrar como sería el flujo de esta solución frente a un mensaje de error tradicional.
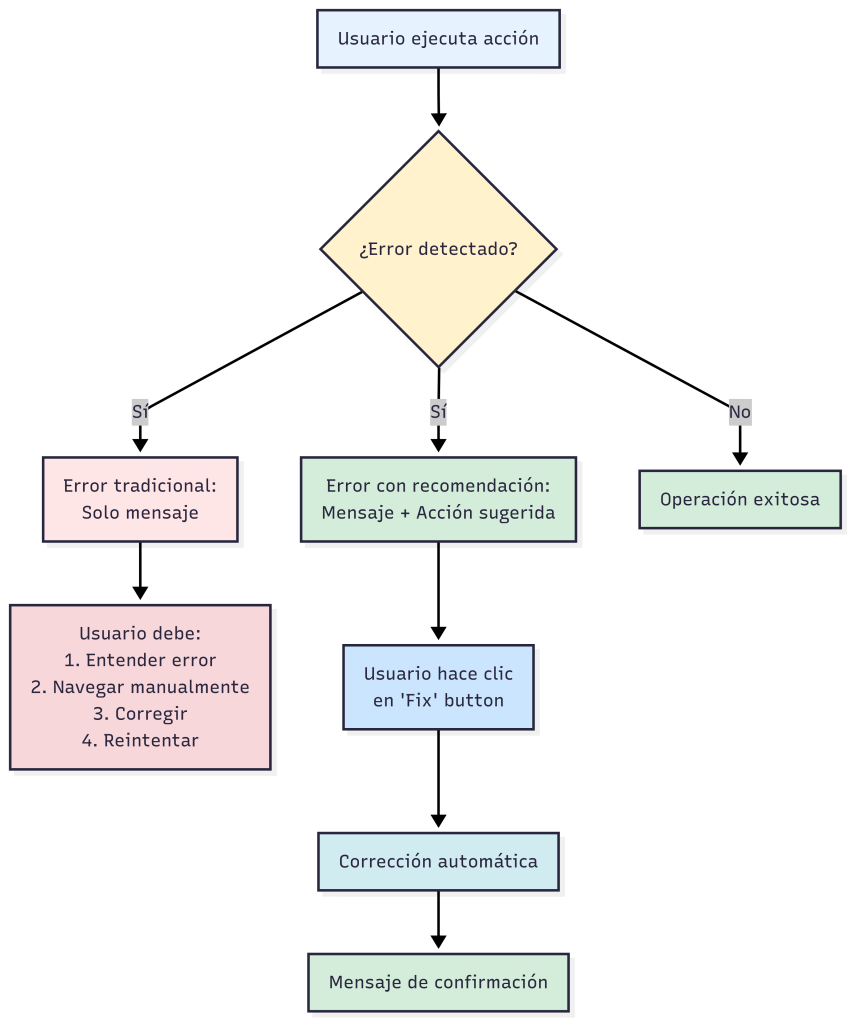
Pongamos un ejemplo sencillo para entenderlo: Un usuario intenta contabilizar un asiento que incluye una cuenta contable bloqueada. Con esta funcionalidad, el escenario podría ser el siguiente:
- Error detectado: «GL Account 40200 is blocked».
- Acción sugerida: «Unblock Account» (botón visible).
- Corrección inmediata: Un clic desbloquea la cuenta automáticamente.
- Confirmación: «GL Account 40200 unblocked».
Recordemos que es un ejemplo, es probable que no podamos desbloquear alegremente las cuentas contables de una empresa. La idea es demostrar la potencialidad de la funcionalidad.

La arquitectura de la solución se apoya en lo siguiente:
- Interfaz ErrorMessageFix que define tres métodos principales:
interface ErrorMessageFix
{
/// <summary>
/// Configura las propiedades del mensaje de error
/// </summary>
procedure OnSetErrorMessageProps(var ErrorMessage: Record "Error Message" temporary);
/// <summary>
/// Ejecuta la corrección automática del error
/// </summary>
procedure OnFixError(ErrorMessage: Record "Error Message" temporary): Boolean;
/// <summary>
/// Retorna un mensaje de éxito después de la corrección
/// </summary>
procedure OnSuccessMessage(): Text;
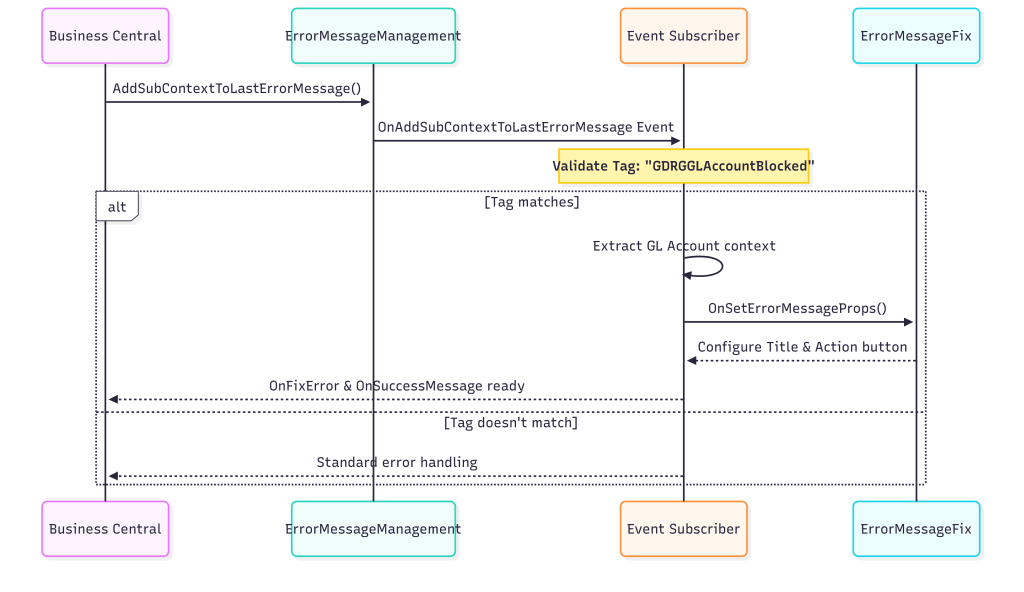
}- El Event Subscriber automático actúa como un filtro que intercepta errores de Business Central. Valida si el Tag corresponde a nuestra implementación y, si coincide, extrae el registro problemático del contexto, configura las propiedades del Error Message con el ID del registro y campo involucrado, e invoca la interfaz ErrorMessageFix para establecer el título del error y botón de acción.
[EventSubscriber(ObjectType::Codeunit, Codeunit::"Error Message Management",
OnAddSubContextToLastErrorMessage, '', false, false)]
local procedure OnAddSubContextToLastErrorMessage(Tag: Text; VariantRec: Variant;
var ErrorMessage: Record "Error Message" temporary)
var
RecordToFix: Record "Your Target Table";
RecRef: RecordRef;
IErrorMessageFix: Interface ErrorMessageFix;
ErrorMsgFixImplementation: Enum "Error Msg. Fix Implementation";
begin
// 1. Define which implementation this subscriber handles
ErrorMsgFixImplementation := Enum::"Error Msg. Fix Implementation"::YourImplementation;
if Tag <> Format(ErrorMsgFixImplementation) then
exit;
// 2. Extract the record context from the error
if VariantRec.IsRecord() then begin
RecRef.GetTable(VariantRec);
if RecRef.Number() = Database::"Your Target Table" then begin
RecRef.SetTable(RecordToFix);
// 3. Configure the Error Message properties
ErrorMessage.Validate("Sub-Context Record ID", RecordToFix.RecordId());
ErrorMessage.Validate("Sub-Context Field Number", RecordToFix.FieldNo("Problem Field"));
ErrorMessage.Validate("Error Msg. Fix Implementation", ErrorMsgFixImplementation);
// 4. Call the interface to set up the error message
IErrorMessageFix := ErrorMessage."Error Msg. Fix Implementation";
IErrorMessageFix.OnSetErrorMessageProps(ErrorMessage);
ErrorMessage.Modify(false);
end;
end;
end;- Triggering los errores en código, utilizaremos «
Error Message Management» que permite logging contextual con recomendaciones automáticas.
procedure LogFieldValidationError(RecordVar: Variant; FieldNo: Integer; ErrorMessage: Text; FixMyImplementation: Enum "Error Msg. Fix Implementation"): Boolean
var
ErrorMessageMgt: Codeunit "Error Message Management";
begin
if ErrorMessageMgt.IsActive() then begin
// Registrar el error contextual con el campo específico
ErrorMessageMgt.LogContextFieldError(0, ErrorMessage, RecordVar, FieldNo, '');
// Asociar la implementación de fix específica
ErrorMessageMgt.AddSubContextToLastErrorMessage(Format(FixMyImplementation), RecordVar);
end;
exit(true);
end;
procedure DemoValidateAndShowErrors(RecordVar: Variant; FieldNo: Integer; ErrorMessage: Text; FixMyImplementation: Enum "Error Msg. Fix Implementation"; RecordName: Text)
var
ErrorMessageHandler: Codeunit "Error Message Handler";
ErrorMessageMgt: Codeunit "Error Message Management";
HasErrors: Boolean;
begin
// Activar el sistema de manejo de errores
ErrorMessageMgt.Activate(ErrorMessageHandler);
// Ejecutar validación usando LogFieldValidationError directamente
HasErrors := LogFieldValidationError(RecordVar, FieldNo, ErrorMessage, FixMyImplementation);
// Mostrar errores si los hay
if HasErrors then begin
if ErrorMessageMgt.GetLastErrorID() > 0 then
ErrorMessageHandler.ShowErrors() // Mostrar página con recomendaciones
else
Message('Error occurred but could not retrieve details.');
end else
Message('%1 validation passed successfully.', RecordName);
end;Veamos como todos los componente anteriores trabajan juntos:
¿Cómo lo probamos? Tenemos una página de pruebas que permite simular y validar fácilmente unos escenarios de error. La interfaz muestra el estado actual del GL Account 6240002 (Fuel) y proporciona botones específicos para probar cada tipo de corrección automática:
- Setup Blocked Account Test: Configura la cuenta 6240002 como bloqueada (Blocked = Yes) para preparar el escenario de prueba.
- Setup Direct Posting Test: Desactiva Direct Posting en la cuenta 6240002 para simular un segundo escenario.
- Validate Account: Ejecuta la validación que dispara los errores.
- Reset Account to Valid State: Restaura la cuenta a su estado original (desbloqueada y con Direct Posting habilitado).

Ante un error, en la siguiente imagen veríamos el flujo:
- Error inicial detectado: «Account 6240002 is blocked» aparece en la lista de Error Messages.
- Acción recomendada disponible: El botón «Accept recommended action» y «Unblock Account» (resaltados en rojo) están visibles y listos para ser ejecutados.
- Confirmación de éxito: El mensaje «GL Account 6240002 unblocked» confirma que la corrección se aplicó exitosamente.
- Estado final actualizado: El error ahora muestra Status: «Fixed» (resaltado en verde), indicando que el problema fue resuelto automáticamente.

Los beneficios de esta funcionalidad son realmente significativos cuando sabemos gestionarla, implementarla y entenderla correctamente. Sin embargo, en entornos empresariales críticos, no todas las correcciones automáticas deberían ejecutarse inmediatamente sin supervisión.
Para que funcione adecuadamente, debemos tener instalada la aplicación (extensión) «Error Messages with Recommendations».
El código se encuentra aquí, por si quieres revisarlo: Blog/GDRGDev_ErrorMgtWithRecommendation at main · gdrgdev/Blog
Los objetos son los siguientes:
- GDRGGLAccountBlockedError.Codeunit.al: Implementación para manejar errores de cuentas bloqueadas.
- GDRGGLAccDirectPostError.Codeunit.al: Implementación para errores de Direct Posting deshabilitado.
- GDRGGLAccountErrorGen.Codeunit.al: Generador de errores para pruebas y simulaciones.
- GDRGErrorTestCard.Page.al: Página de pruebas para simular diferentes escenarios de error.
- GDRGErrorMsgFixImpl.EnumExt.al: Extensión del enum para registrar nuestras implementaciones.
- GDRGErrorMsgFix.PermissionSet.al: Conjunto de permisos necesarios para el framework.
Espero que esta información te ayude.
🔧 Transforming BC Error Handling with Smart Recommendations 📝
We will continue discussing error management and how we can leverage the patterns and functionalities offered by Business Central. Now, we will explore Microsoft’s «Error Messages with Recommendations« application (extension), a very useful and versatile feature that allows us to transform an error message into an immediate solution with just one click.
The centralized «Error Messages» page serves as the control center where users can view all errors and take corrective actions directly. This application allows us to create extensions that automatically capture errors and offer intelligent solutions. The application enables:
- Automatically detect the specific problem.
- Suggest a clear corrective action.
- Allow immediate resolution with a single click.
- Confirm the solution with a success message.
We could show how this solution would work compared to a traditional error message.

Let’s take a simple example to illustrate this: A user tries to post an accounting entry that includes a blocked accounting account. With this functionality, the scenario could be as follows:
- Error detected: «GL Account 40200 is blocked».
- Suggested action: «Unblock Account» (button visible).
- Immediate correction: One click will automatically unblock the account.
- Confirmation: «GL Account 40200 unblocked».
Let’s remember that this is just an example; we probably can’t simply unlock a company’s accounting records. The idea is to demonstrate the potential of this feature.

The solution architecture is based on the following:
- ErrorMessageFix interface that defines three main methods:
interface ErrorMessageFix
{
/// <summary>
/// Configures error message properties
/// </summary>
procedure OnSetErrorMessageProps(var ErrorMessage: Record "Error Message" temporary);
/// <summary>
/// Executes automatic error correction
/// </summary>
procedure OnFixError(ErrorMessage: Record "Error Message" temporary): Boolean;
/// <summary>
/// Returns a success message after correction
/// </summary>
procedure OnSuccessMessage(): Text;
}- The automatic Event Subscriber acts as a filter that intercepts errors from Business Central. It verifies if the tag matches our implementation, and if it does, it extracts the problematic record from the context, sets the properties of the Error Message with the record ID and the affected field, and then invokes the ErrorMessageFix interface to set the error title and action button.
[EventSubscriber(ObjectType::Codeunit, Codeunit::"Error Message Management",
OnAddSubContextToLastErrorMessage, '', false, false)]
local procedure OnAddSubContextToLastErrorMessage(Tag: Text; VariantRec: Variant;
var ErrorMessage: Record "Error Message" temporary)
var
RecordToFix: Record "Your Target Table";
RecRef: RecordRef;
IErrorMessageFix: Interface ErrorMessageFix;
ErrorMsgFixImplementation: Enum "Error Msg. Fix Implementation";
begin
// 1. Define which implementation this subscriber handles
ErrorMsgFixImplementation := Enum::"Error Msg. Fix Implementation"::YourImplementation;
if Tag <> Format(ErrorMsgFixImplementation) then
exit;
// 2. Extract the record context from the error
if VariantRec.IsRecord() then begin
RecRef.GetTable(VariantRec);
if RecRef.Number() = Database::"Your Target Table" then begin
RecRef.SetTable(RecordToFix);
// 3. Configure the Error Message properties
ErrorMessage.Validate("Sub-Context Record ID", RecordToFix.RecordId());
ErrorMessage.Validate("Sub-Context Field Number", RecordToFix.FieldNo("Problem Field"));
ErrorMessage.Validate("Error Msg. Fix Implementation", ErrorMsgFixImplementation);
// 4. Call the interface to set up the error message
IErrorMessageFix := ErrorMessage."Error Msg. Fix Implementation";
IErrorMessageFix.OnSetErrorMessageProps(ErrorMessage);
ErrorMessage.Modify(false);
end;
end;
end;- To trigger errors in the code, we will use «Error Message Management,» which allows contextual logging with automatic recommendations.
procedure LogFieldValidationError(RecordVar: Variant; FieldNo: Integer; ErrorMessage: Text; FixMyImplementation: Enum "Error Msg. Fix Implementation"): Boolean
var
ErrorMessageMgt: Codeunit "Error Message Management";
begin
if ErrorMessageMgt.IsActive() then begin
// Register contextual error with specific field
ErrorMessageMgt.LogContextFieldError(0, ErrorMessage, RecordVar, FieldNo, '');
// Associate specific fix implementation
ErrorMessageMgt.AddSubContextToLastErrorMessage(Format(FixMyImplementation), RecordVar);
end;
exit(true);
end;
procedure DemoValidateAndShowErrors(RecordVar: Variant; FieldNo: Integer; ErrorMessage: Text; FixMyImplementation: Enum "Error Msg. Fix Implementation"; RecordName: Text)
var
ErrorMessageHandler: Codeunit "Error Message Handler";
ErrorMessageMgt: Codeunit "Error Message Management";
HasErrors: Boolean;
begin
// Activate error handling system
ErrorMessageMgt.Activate(ErrorMessageHandler);
// Execute validation using LogFieldValidationError directly
HasErrors := LogFieldValidationError(RecordVar, FieldNo, ErrorMessage, FixMyImplementation);
// Show errors if any
if HasErrors then begin
if ErrorMessageMgt.GetLastErrorID() > 0 then
ErrorMessageHandler.ShowErrors() // Show page with recommendations
else
Message('Error occurred but could not retrieve details.');
end else
Message('%1 validation passed successfully.', RecordName);
end;Let’s see how all the components above work together:

How do we test it? We have a test page that allows us to easily simulate and validate error scenarios. The interface displays the current status of GL Account 6240002 (Fuel) and provides specific buttons to test each type of automatic correction:
- Setup Blocked Account Test: Set account 6240002 as blocked (Blocked = Yes) to prepare for the test scenario.
- Setup Direct Posting Test: Disable Direct Posting for account 6240002 to simulate a second scenario.
- Validate Account: Run the validation process to trigger any errors.
- Reset Account to Valid State: Restore the account to its original state (unblocked and with Direct Posting enabled).

In case of an error, the following image shows the process flow:
- Initial error detected: «Account 6240002 is blocked» appears in the list of error messages.
- Recommended action available: The «Accept recommended action» and «Unblock Account» buttons (highlighted in red) are visible and ready to be executed.
- Success confirmation: The message «GL Account 6240002 unblocked» confirms that the fix was successfully applied.
- Updated status: The error now shows Status: «Fixed» (highlighted in green), indicating that the problem was resolved automatically.

The benefits of this functionality are truly significant when we know how to manage, implement, and understand it correctly. However, in critical business environments, not all automatic fixes should be executed immediately without supervision.
For it to work properly, we need to have the application (extension) installed. «Error Messages with Recommendations».
The code is here, if you want to check it out: Blog/GDRGDev_ErrorMgtWithRecommendation at main · gdrgdev/Blog
The objects are as follows:
- GDRGGLAccountBlockedError.Codeunit.al: Implementation to handle blocked account errors.
- GDRGGLAccDirectPostError.Codeunit.al: Implementation for Direct Posting disabled errors.
- GDRGGLAccountErrorGen.Codeunit.al: Error generator for testing and simulations.
- GDRGErrorTestCard.Page.al: Test page to simulate different error scenarios.
- GDRGErrorMsgFixImpl.EnumExt.al: Enum extension to register our implementations.
- GDRGErrorMsgFix.PermissionSet.al: Permission set required for the extension.
I hope this information helps you.
Más información / More information:


Deja un comentario